Trump told reporters he will use executive power to ban TikTok
NEWSPresident Donald Trump told reporters on Air Force One that he will act as soon as Saturday to ban TikTok from the US, CNBC reported.
The story is updating.
President Donald Trump told reporters on Air Force One that he will act as soon as Saturday to ban TikTok from the US, CNBC reported.
The story is updating.
Even the hard-charging world of early-stage startups has its share of procrastinators, lollygaggers, slow-pokes, wafflers and last-minute decision makers. If that’s your demographic, today is your lucky day.
You now have an extra week (courtesy of Saint Expeditus, the patron saint of procrastinators), to score early-bird savings to Disrupt 2020, which takes place September 14-18. Buy your pass before the new and final deadline — August 7 at 11:59 p.m. (PT) — and save up to $300. Who says prayers (or secular entreaties) go unanswered?
Your pass opens the door to five days of Disrupt — the biggest, longest TechCrunch conference ever. Drawing thousands of attendees and hundreds of innovative early-stage startups from around the world, you won’t find a better time, place or opportunity to accelerate the speed of your business.
Here are four world-class reasons to attend Disrupt 2020.
World-class speakers. Hear and engage with leading voices in tech, business and investment across the Disrupt stages. Folks like Sequoia Capital’s Roelof Botha, Ureeka’s Melissa Bradley and Slack’s Tamar Yehoshua — to name just a few. Here’s what you can see onstage so far.
World-class startups. Explore hundreds of innovative startups exhibiting in Digital Startup Alley — including the TC Top Picks. This elite cadre made it through our stringent screening process to earn the coveted designation, and you’ll be hard-pressed to find a more varied and interesting set of startups.
World-class networking. CrunchMatch, our AI-powered networking platform, simplifies connecting with founders, potential customers, R&D teams, engineers or investors. Schedule 1:1 video meetings and hold recruitment or extended pitch sessions. CrunchMatch launches weeks before Disrupt to give you more time to scout, vet and schedule.
World-class pitching. Don’t miss Startup Battlefield, the always-epic pitch competition that’s launched more than 900 startups, including big-time names like TripIt, Mint, Dropbox and many others. This year’s crop of startups promises to throw down hard for bragging rights and the $100,000 cash prize.
Need another reason to go? Take a page out of SIMBA Chain founder Joel Neidig’s playbook:
Our primary goal was to make people aware of the SIMBA Chain platform capabilities. Attending Disrupt is great way to get your name out there and build your customer base.
It’s time for all you last-minute lollygaggers to get moving and take advantage of this second, final chance to save up to $300. Buy your pass before August 7 at 11:59 p.m. (PT).
Is your company interested in sponsoring or exhibiting at Disrupt 2020? Contact our sponsorship sales team by filling out this form.
Here they are, ranked by how much weight we put behind them:
Hillsborough State Attorney Andrew Warren announced today that he has filed 30 felony charges against a 17-year-old resident of Tampa, Florida, who was described by the state attorney’s office as “the mastermind of the recent hack of Twitter.”
The hack in question occurred earlier this month and involved high-profile Twitter users like Apple, Elon Musk, Joe Biden and Barack Obama, whose accounts all posted messages promoting a Bitcoin wallet and claiming, “All Bitcoin sent to the address below will be sent back doubled!”
The teen (we’re not identifying them because they’re a minor) allegedly made more than $100,000 through this cryptocurrency scam.
The state attorney’s office said that the teen was arrested earlier today as a result of an investigation by the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the U.S. Department of Justice, and that they will be tried as an adult. They face charges including one count of organized fraud (over $50,000) and 17 counts of communications fraud (over $300).
“These crimes were perpetrated using the names of famous people and celebrities, but they’re not the primary victims here,” Warren said in a statement. “This ‘Bit-Con’ was designed to steal money from regular Americans from all over the country, including here in Florida. This massive fraud was orchestrated right here in our backyard, and we will not stand for that.”
As we reported at the time, the hack used Twitter’s own admin tool to gain access to high-profile accounts. The company just updated its blog post outlining what it knows about the attack:
The social engineering that occurred on July 15, 2020, targeted a small number of employees through a phone spear phishing attack A successful attack required the attackers to obtain access to both our internal network as well as specific employee credentials that granted them access to our internal support tools. Not all of the employees that were initially targeted had permissions to use account management tools, but the attackers used their credentials to access our internal systems and gain information about our processes. This knowledge then enabled them to target additional employees who did have access to our account support tools. Using the credentials of employees with access to these tools, the attackers targeted 130 Twitter accounts, ultimately Tweeting from 45, accessing the DM inbox of 36, and downloading the Twitter Data of 7.
To prevent a similar attack from succeeding in the future, Twitter said it will be “accelerating several of our pre-existing security workstreams and improvements to our tools” and also improving the methods it uses to detect and stop inappropriate access to its internal systems.
Google Vice President of Engineering Dave Burke provided an update about the Exposure Notifications System (ENS) that Google developed in partnership with Apple as a way to help public health authorities supplement contact-tracing efforts with a connected solution that preserves privacy while alerting people of potential exposure to confirmed cases of COVID-19. In the update, Burke notes that the company expects “to see the first set of these apps roll out in the coming weeks” in the U.S., which may be a tacit response to some critics who have pointed out that we haven’t seen much in the way of actual products being built on the technology that was launched in May.
Burke writes that 20 states and territories across the U.S. are currently “exploring” apps that make use of the ENS system, and that together those represent nearly half (45%) of the overall American populace. He also shared recent updates and improvements made to both the Exposure Notification API as well as to its surrounding documentation and information that the companies have shared in order to answer questions from state health agencies, and hopefully make its use and privacy implications more transparent.
The ENS API now supports exposure notifications between countries, which Burke says is a feature added based on nations that have already launched apps based on the tech (that includes Canada, as of today, as well as some European nations). It’s also now better at using Bluetooth values specific to a wider range of devices to improve nearby device detection accuracy. He also says they’ve improved the reliability for both apps and debugging tools for those working on development, which should help public health authorities and their developer partners more easily build apps that actually use ENS.
Burke continues that there’s been feedback from developers that they’d like more detail about how ENS works under the covers, and so they’ve published public-facing guides that direct health authorities about test verification server creation, code revealing its underlying workings and information about what data is actually collected (in a de-identified manner) to allow for much more transparent debugging and verification of proper app functioning.
Google also explains why it requires that an Android device’s location setting be turned on to use Exposure Notifications — even though apps built using the API are explicitly forbidden from also collecting location data. Basically, it’s a legacy requirement that Google is removing in Android 11, which is set to be released soon. In the meantime, however, Burke says that even with location services turned off, no app that uses the ENS will actually be able to see or receive any location data.
Owning one brick-and-mortar business seems complicated enough. But running multiple locations? For many owners, that’s a constant juggling act of phone calls, check lists, and driving back and forth from store to store. In the middle of a pandemic, it gets all the more complex.
Delightree, a company out of the previous Alchemist Accelerator class, has raised $3M to build a tool hyper focused on helping owners of franchise businesses (think hotels, gyms, restaurant chains, etc) take their operations and workflows digital.
A big part of the idea with Delightree is to move much of what currently happens through pen-and-paper checklists over to smartphones, allowing franchise owners to know what’s going at their locations from afar. They digitize workflows like the daily store opening/closing procedures or maintenance routines, with employees checking boxes on their devices rather than a paper todo list. If something gets missed along the way, Delightree can automatically ping the owner to let them know before it becomes an issue.
They’ll also help to automate and track things like onboarding new employees and staying prepared for inspections, while giving owners a centralized place to make team wide announcements or contact employees.
Delightree evolved out of a previous company built by its co-founders, Madhulika Mukherjee and Tushar Mishra. They’d been working on Survaider, a tool that monitored customer feedback across social media, review sites, etc, and turned that feedback into actionable to-do lists.
“When we were piloting it, our customers started saying: can we create our own tasks? Or can I tell something to my employees through this?” Mishra told me. “It was just such an obvious problem, so we started building Delightree.”

Delightree co-founders Tushar Mishra and Madhulika Mukherjee
The team has also been working on a feature they call Delightcomply, which helps stores stay up to date on the latest CDC guidelines for businesses operating through the pandemic, and to automatically share compliance details with potential customers. A business could use Delightcomply to publicly outline the steps it’s taking to keep employees/customer safe, for example, with the listing automatically updated to show the status of each task.
Delightree is currently working directly with each new customer to help them through the initial setup — specifically, to help franchisees take the standard operating procedures they receive directly from the brand owners and turn them into Delightree workflows. They’re still working out their exact pricing model, but say that they charge on a per-location-per-month basis with pricing varying depending on the size/complexity of the business. They’ve set up waitlist for anyone interested.
This $3 million seed round was funded by Accel Partners, Emergent Ventures, Brainstorm Ventures, Axilor Ventures, and Alchemist. As part of the deal, Emergent partner Anupam Rastogi has joined Delightree’s board of directors.
President Trump has plans to order China’s ByteDance, the owner of hit social video app TikTok, to divest from the company, according to new reporting from Bloomberg. The app is increasingly a target of U.S. security concerns over its Chinese ownership.
After the initial news, reports bubbled up that Microsoft is in talks to buy the Chinese social network, which is potentially valued at $50 billion and has a massive footprint in the U.S. TikTok itself is not available in China and Chinese users instead use Douyin, a similar Bytedance-owned app specific to the country.
While little is known about what that could mean — or if it’s how a sale of TikTok would really take place — the event would send huge waves through the tech world. TikTok is one of the only meaningful outside competitors for U.S.-based social networks like YouTube and Facebook.
It would certainly be strange timing were an American tech giant to purchase TikTok: On Wednesday, a Congressional committee held a high-profile hearing scrutinizing tech’s biggest mergers and acquisitions. The White House declined to comment on the report when contacted by TechCrunch.
TikTok has come under increased government scrutiny recently, with the president expressing interest in banning the app outright in the U.S. This month, Joe Biden’s campaign asked its staffers to delete the app from both work and personal devices.
Some U.S. companies have also banned their employees from using the app over concerns about its Chinese ownership.
Nearly 500 pages of evidence were made public during the House Judiciary’s marathon hearing this week on potential anti-competitive actions by Amazon, Facebook, Google and Apple. We’ve collected them here with added context and an omnibus, searchable version for anyone who’d rather not juggle four dozen documents.
The emails, chat logs, and other communications listed here trickled out online as the hearings went on. Many are internal documents that were never meant to be exposed publicly — for instance, Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg telling a colleague that “we can likely always just buy any competitive startups” shortly before acquiring Instagram in 2012.
Congressional investigators wield considerable power in compelling the release of such documents, even against the will of the companies, which would almost certainly never provide such self-incriminating information to journalists. As such these documents contain all manner of useful information, most of it providing insight into the the otherwise opaque thinking of executives as their companies made key decisions about growing their businesses — and hint at strategies traditionally employed by monopolies.
While there isn’t anything that could be called a smoking gun, these are not the only evidence the investigation collected, only those it needed to make public for this hearing. Legislators spoke of other documents and also of interviews and testimony that corroborated their allegations, or contradicted companies’ accounts of events.
While there are too many documents to discuss individually, we’ve noted some interesting exchanges we’ve come across in the files for each company. A combined, searchable mega-file of the internal documents can be found at the bottom of this post. It’s not in any particular order, so it’s best to sift through by looking for key terms, key figures and company names.
The documents contain internal communications about Amazon’s pursuit and eventual purchase of Diapers.com, which also came up in the hearing itself. Aggressive price cutting by the former forced the latter out of business, allowing it to be snapped up and integrated. In one document, we see that Amazon discusses setting up special automatic pricing rules that more aggressively undercut Diapers.com prices compared to other sellers of diapers and toys.
Another document shows that Amazon lost in the neighborhood of $200M in a single quarter during this period, showing that it was willing to take on losses at a scale that the smaller business couldn’t possibly withstand — a classic monopolistic tactic only possible if you command a giant chunk of a market. Rep. Scanlon (D-PA) pushed Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos on this at about the 2 hour 15 minute mark.
Jeff Bezos, spurred by a TechCrunch post, asks what the plan is for Diapers.com’s next play, Soap.com, and receives a summary of the existing plan, which “undercuts the core diapers business for diapers.com,” and “will slow the adoption of soap.com.” This email shows how Amazon acknowledged that it has positioned itself as “the place to sell globally,” particularly with manufacturers from China who wanted direct access to American consumers. A deck of Diapers.com metrics mentions “predatory pricing” and Amazon as very specific threats to their short- and long-term plans.
Regarding Amazon’s purchase of Ring, which might have emerged as a smart home competitor, this document shows senior management discussing being “willing to pay for market position as it’s hard to catch the leader.” Another email offers more context on Amazon’s thoughts on the acquisition of Ring (at the time referred to as Project Darwin) before it went through. Bezos himself says in this exchange that “we’re buying market position — not technology. And that market position and momentum is very valuable.”
In an email exchange from March 2012, the month before Facebook announced it would buy Instagram, Zuckerberg shares a conversation about China’s “strong culture of cloning things quickly.”
In the original conversation, sent to Facebook Product lead Chris Cox and CTO Mike Schroepfer, a high level Facebook employee describes how they met with the founders of Chinese company RenRen who described how their own company copied apps like Voxer and Pinterest. The author comments that it’s easier for those companies to get products out quickly “since they’re copying other people” and goes on to suggest how a similar strategy could work for Facebook. Forwarding the email to Sheryl Sandberg, Zuckerberg comments “You’ll probably find this interesting and agree.”
Another set of documents captures Mark Zuckerberg’s private courtship of Instagram co-founder Kevin Systrom. Tellingly, a side conversation between Systrom and a former Facebook product VP shows that the Instagram creator was concerned about Zuckerberg going into “destroy mode” if Systrom didn’t agree to sell. There’s also more insight about how Facebook saw the Instagram deal and how the company decided to keep it as separate product.
The Facebook documents also include some conversation about the WhatsApp acquisition, which it nicknames “Project Cobalt” including the minutes from a board meeting four days before Facebook went public with its acquisition plans. “Ms. Sandberg emphasized that the high concentration of the mobile operating system market — with two providers serving the vast majority of smartphone users around the world — poses a significant strategic threat to [Facebook’s] business…” the minutes state.
Apple’s isn’t as well-known for crushing competitors as the other three companies, but it certainly likes to wring revenues out of its software partners while handling maintaining a tight grip on both its hardware and software. Many of the documents focus on Apple’s internal strategies responding to criticism on issues like the right-to-repair controversy and developers unhappy with the obsessive level of control Apple exercises over its products.
The Apple documents also detail how the App Store creator gives preferential treatment to some companies on the commissions it takes. In 2016 emails between Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos and Apple SVP Eddy Cue, Apple looks to have struck a special deal over the Amazon Prime Video app for iOS and Apple TV.
An email exchange back in 2011 also details how Apple mulled raising commissions to 40% for the first year for subscription apps. “I think we may be leaving money on the table if we just asked for about 30% of the first year of sub,” Cue wrote. This didn’t come to pass, but the correspondence does provide insight into some questions about setting its own rules that the company didn’t really have an answer to in the hearing.
In a confidential internal presentation from 2006, Google raises alarm about the “orthogonal threat” posed by social networks and other websites with “high entertainment value,” like YouTube.
“… The team developed an opinion that these social networking sites will ultimately represent a threat to our search business as people will spend more time on those sites and ultimately may do most searches from the search boxes available there. They aren’t direct competitors, but they may displace us in end-user time tradeoff.”
The presentation goes on to argue that Google should “own the search box on the entertainment sites” and develop its own social networking solution so those sites don’t win out. That same year, Google announced its landmark acquisition of YouTube.
Other email chains from around the same time capture Google’s internal thinking in the run-up to buying YouTube.
“YouTube’s value to us would be a smart team and a platform we could build from (maybe enough to justify an acquisition on its own), but would we really be able to preserve their community once we start reviewing and pulling copyright or inappropriate content? If anything, that’s likely to cast a poor light on Google,” then-Google Director of Product Hunter Walk wrote, in an interesting moment foreshadowing Google’s current content moderation woes.
After floating a $200 million deal for the company and having YouTube turn up its nose, Google eventually went on to buy the now-ubiquitous video sharing platform for $1.65 billion.
You can read and search through the documents here:
House Antitrust Subcommitte… by TechCrunch on Scribd
As the Internet of Things proliferates, security cameras are getting smarter. Today, these devices have machine learning capability that helps the camera automatically identify what it’s looking at — for instance, an animal or a human intruder? Today, Cisco announced that it has acquired Swedish startup Modcam and is making it part of its Meraki smart camera portfolio with the goal of incorporating Modcam computer vision technology into its portfolio.
The companies did not reveal the purchase price, but Cisco tells us that the acquisition has closed.
In a blog post announcing the deal, Cisco Meraki’s Chris Stori says Modcam is going to up Meraki’s machine learning game, while giving it some key engineering talent, as well.
“In acquiring Modcam, Cisco is investing in a team of highly talented engineers who bring a wealth of expertise in machine learning, computer vision and cloud-managed cameras. Modcam has developed a solution that enables cameras to become even smarter,” he wrote.
What he means is that today, while Meraki has smart cameras that include motion detection and machine learning capabilities, this is limited to single camera operation. What Modcam brings is the added ability to gather information and apply machine learning across multiple cameras, greatly enhancing the camera’s capabilities.
“With Modcam’s technology, this micro-level information can be stitched together, enabling multiple cameras to provide a macro-level view of the real world,” Stori wrote. In practice, as an example, that could provide a more complete view of space availability for facilities management teams, an especially important scenario as businesses try to find safer ways to open during the pandemic. The other scenario Modcam was selling was giving a more complete picture of what was happening on the factory floor.
All of Modcams employees, which Cisco described only as “a small team,” have joined Cisco, and the Modcam technology will be folded into the Meraki product line, and will no longer be offered as a standalone product, a Cisco spokesperson told TechCrunch.
Modcam was founded in 2013 and has raised $7.6 million, according to Crunchbase data. Cisco acquired Meraki back in 2012 for $1.2 billion.
Australia is closing in on a legally binding framework to force adtech giants Facebook and Google pay media companies for monetizing their news content when it’s posted to their social media platforms or otherwise aggregated and monetized.
Back in April the country’s government announced it would adopt a mandatory code requiring the tech giants to share ad revenue with media business after an attempt to negotiate a voluntary arrangement with the companies failed to make progress.
Today Australia’s Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) has published details of a first pass at that mandatory code — which it says is intended to address “acute bargaining power imbalances” between local news businesses vs the adtech duopoly, Google and Facebook.
The draft follows a consultation process before and after the release of a concepts paper in May, in which the ACCC sought feedback on a range of options. More than 40 submissions were received, it said.
Under the proposed code the ACCC is suggesting a binding “final offer” arbitration process as a way to avoid platforms seeking to drag payment negotiations. Under the proposal they’d get three months’ “negotiation and mediation”, after which an independent arbitrator would choose which of the two parties’ final offer is “the most reasonable”, doing so within 45 business days.
“This would ensure disagreements about payment for content are resolved quickly. Deals on payment could be reached within six months of the code coming into effect if arbitration is required,” the ACCC writes.
The code also aims to enable groups of media businesses (such as local and regional publications) to collectively negotiate to get a better deal out of platforms use of their content.
On the enforcement front, the draft proposes that non-compliance — such as not bargaining in good faith or breaching minimum commitments — can lead to infringement penalties, with the maximum set at $10M or 3x the benefit obtained or 10% of a platform’s turnover in the market in the last 12 months (whichever is greater). So Facebook and Google could potentially be on the hook for fines running to many millions of dollars if they are found to have breached such a code.
The scope of the code’s application looks broadly enough drawn that it seems intended to try to prevent platforms from dodging payment by simply switching off a single news-focused products (such as Google News). Google did just that in Spain instead of paying for reuse of news snippets there (and it remains switched off in the market). But the ACCC’s proposal also applies to Google search and Discover so Google would have to forgo showing any Australian news content to avoid the revenue share — which is a far bigger switch to flip.
Another interesting aspect of the proposal would require the platforms to give news media businesses around a month (28 days’) notice of algorithm changes that are “likely to materially affect” referral traffic to news and/or the ranking of news behind paywalls; and also for “substantial” changes to the display and presentation of news, and advertising directly associated with news.
Another notable requirement is for platforms to give news media businesses “clear information” about the data they collect via users’ interactions with news content on their platforms — such as how long people spend on an article; how many articles they consume in a certain time period; and other data about user engagement with news across platform services.
This aspect of the proposal looks intended to tackle the problem of dominant platforms using their market power to maintain their grip on the attention economy by being able to monopolize access to data by blocking content producers from being able to access information about how Internet users are engaging with their work.
Platforms like Facebook have sought to centralize others’ content to their advantage — applying market power to encourage content to be posted in a place where only they have full access to interaction data. This breaks the link between news producers and their own audience, making it harder for them to perform analytics around articles or respond to changes and trends in consumption behavior.
Being cut off from so much user data also makes it harder for media outlets to cultivate closer relations with consumers of their product — something that looks increasingly vital for developing successful additional revenue streams, such as subscription offers, for example.
“There is a fundamental bargaining power imbalance between news media businesses and the major digital platforms, partly because news businesses have no option but to deal with the platforms, and have had little ability to negotiate over payment for their content or other issues,” said ACCC chair, Rod Sims, commenting on the proposal in a statement.
“In developing our draft code, we observed and learned from the approaches of regulators and policymakers internationally that have sought to secure payment for news. We wanted a model that would address this bargaining power imbalance and result in fair payment for content, which avoided unproductive and drawn-out negotiations, and wouldn’t reduce the availability of Australian news on Google and Facebook.”
“We believe our proposed draft code achieves these purposes,” he added.
Google and Facebook could not work without the content that newspapers, e-commerce, marketplaces and others provide. If you agree with the premise that they have platform monopolies & control the traffic, then regulation & taxation are inevitable. https://t.co/gYLUPZLICP
— Johannes Reck (@JohannesReck) July 31, 2020
The proposal contains more suggestions aimed at breaking down the power imbalance between the two adtech giants and news producers. One element would require them to publish proposals for recognizing original news content on their services — which sounds like an ‘exclusive’ label (to go alongside ‘fact-checked’ labels platforms can sometimes choose to apply).
The pair would also need to provide news media businesses with what the ACCC dubs “flexible user comment moderation tools” — such as the ability to turn off comments on individual stories posted to a platform.
The theme here is increased agency for news businesses vs Facebook and Google so they have a better chance to shape public debate happening around their own content — platforms having also gobbled up the sorts of conversations which used to happen via a newspaper’s letters’ page.
In terms of eligibility, the ACCC says media businesses would be eligible for payment for platforms’ content reuse if the online news content they produce “investigates and explains issues of public significance for Australians” or “issues that engage Australians in public debate and inform democratic decision-making; or issues relating to community and local events”.
Other criteria include adhering to minimum levels of professional editorial standards; maintaining a “suitable degree” of editorial independence; operating in Australia for the main purpose of serving Australian audiences; and generating revenue of more than $150,000 per year.
The code, which would initially only apply to Facebook and Google (though the ACCC notes that other platforms could be added if they gain similar market power), is not intended to capture any non-news content producers, such as drama, entertainment or sports broadcasting.
In a statement responding to the proposal Google expressed deep disappointment. Mel Silva, MD of Google Australia, said:
Our hope was that the Code would be forward thinking and the process would create incentives for both publishers and digital platforms to negotiate and innovate for a better future – so we are deeply disappointed and concerned the draft Code does not achieve this. Instead, the government’s heavy handed intervention threatens to impede Australia’s digital economy and impacts the services we can deliver to Australians.
The Code discounts the already significant value Google provides to news publishers across the board – including sending billions of clicks to Australian news publishers for free every year worth $218 million. It sends a concerning message to businesses and investors that the Australian Government will intervene instead of letting the market work, and undermines Australia’s ambition to become a leading digital economy by 2030. It sets up a perverse disincentive to innovate in the media sector and does nothing to solve the fundamental challenges of creating a business model fit for the digital age.
We urge policymakers to ensure that the final Code is grounded in commercial reality so that it operates in the interests of Australian consumers, preserves the shared benefits created by the web, and does not favour the interests of large publishers at the expense of small publishers.
Facebook had far less to say — sending a line attributed to William Easton, its MD for Australia & New Zealand — which says it’s reviewing the proposal “to understand the impact it will have on the industry, our services and our investment in the news ecosystem in Australia”.
In terms of Australia’s next steps, further consultation will take place on the draft mandatory code during August, with the ACCC saying it will be finalised “shortly after”.
More details about the draft code can be found here.
While regulation being applied to big tech now looks like a given in multiple jurisdictions around the world — with US lawmakers alive to the damage flowing from a handful of hyper-powerful homegrown tech giants— the question of how fair and effective it will be is very much up in the air.
One potentially problematic element of Australia’s approach with this news ad revenue share is that it does not appear to tackle Facebook’s and Google’s abusive model of surveillance capitalism — which remains under regulatory scrutiny in Europe — but seems set to further embed the media with data-mining business models that work by stripping consumers of their privacy to target them with behavioral ads.
Critics contend that a myriad of harms flow from behavioral advertising — from time-wasting clickbait at the low end to democracy-denting disinformation and hate speech at the other. Meanwhile other less intrusive types of ad-targeting are available.
A section of the proposed code that touches on “the privacy of platform users” notes only that: “The draft code’s minimum standards require digital platforms to provide clear information about the data they currently collect through news content. However, the code does not include any requirements for digital platforms to increase sharing of user data with news media businesses. Accordingly, the code does not have an impact on the privacy protections currently applicable to digital platform users.”
Facebook today confirmed it will begin rolling out official music videos across its platform in the U.S., as TechCrunch first reported, as well as introduce a new Music destination within Facebook Watch. The changes, which will go into effect starting this weekend, will allow Facebook users to discover, watch and share music videos from a wide range of artists, including, for example, Anitta, Blake Shelton, Bob Marley, Diplo, Elton John, Jonas Brothers, Josh Groban, Keith Urban, Maren Morris, Marvin Gaye, Miley Cyrus, Nicki Minaj, and others.
Though Facebook had already been working with partners in India and Thailand on a similar music experience before today, the U.S. launch is enabled by Facebook’s expanded partnerships with top labels, including Sony Music, Universal Music Group, Warner Music Group, Merlin, BMG, Kobalt and other independents.
Facebook tells TechCrunch its deals include the full catalog across all major partners and a host of independents.
TechCrunch earlier this month reported Facebook’s plans for music videos would arrive August 1st. We also noted that supported artists were being informed they would soon need to toggle on a new permission that would allow Facebook to automatically add their music videos to their Page, where they could be discovered by fans on the Page’s Videos tab. Once enabled, the artists will be able to edit or remove their video posts at any time.
However, if this setting was not enabled, Facebook will instead automatically generate a separate official music Page on the artist’s behalf, titled “[Artist Name] Official Music,” to enable discovery. That Page would be created and controlled by Facebook and accessible through Facebook Watch, though artists can later choose to opt-in to include their official videos on their own Page.
Image Credits: screenshot via TechCrunch
Image Credits: TechCrunch
With the launch, Facebook users will be able to follow their favorite artists, then receive the latest music video releases from those artists in their News Feed, as they go live. The “follow” option will be available not only on the artist’s Facebook Page, as before, but also directly from the music videos themselves.
By clicking through on the shared posts, fans will be directed to the artist’s Facebook Page, where they can browse the Videos tab to watch more officially licensed music.
The music video posts, like any on Facebook, can be shared, reacted to and commented on. They can also be shared across News Feed, where friends can discover the posts, as well as shared to Groups and in Messenger.
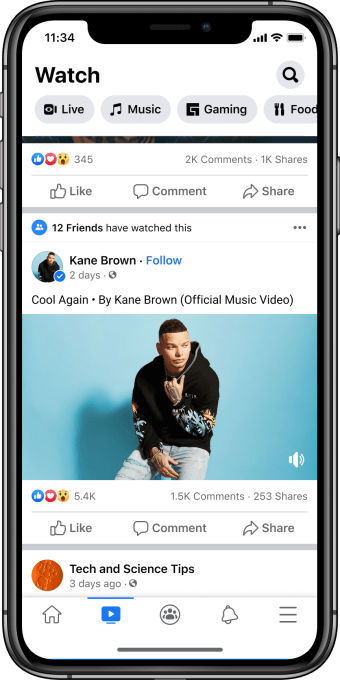
Image Credits: Facebook
The dedicated Music section on Facebook Watch, meanwhile, will allow users to explore music by genre, artist name or mood, or across themed playlists like “Hip Hop MVPs,” “Trailblazers of Pop,” “Epic Dance Videos” or more timely playlists like “Popular This Week” and “New This Week.”
The videos will also be monetized by advertising, like elsewhere on Facebook Watch. However, unlike some video ads, they won’t interrupt the music in the middle of playing. Instead, Facebook tells TechCrunch the ads will either appear pre-roll, during the video as an image ad below the video player or post-roll. These plans may change in the weeks ahead as it iterates on the experience, Facebook notes.
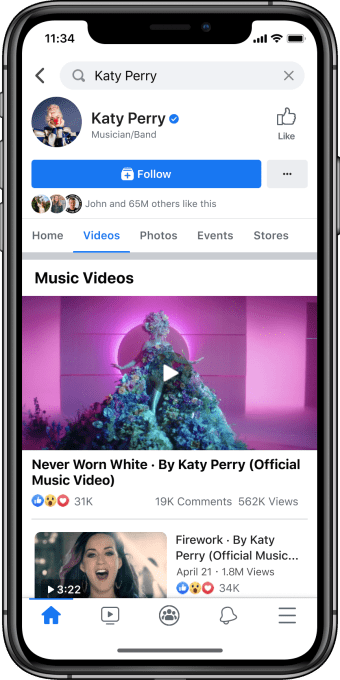
Image Credits: Facebook
The company will apply its personalization technology to the music video experience, too, we understand. As users watch, engage and share, the Music destination in Facebook Watch will become more attuned to your personal likes and interests.
More social experiences are planned for the future, including user-generated playlists.
“Official music videos on Facebook are about more than just watching a video. They’re about social experiences, from discovering new artists with friends to connecting more deeply with artists and people you love,” said Facebook VP of Entertainment, Vijaye Raji. “There’s something in our music video catalog for everyone, and we’re excited for people to discover and rediscover their favorites,” he added.
Facebook says this weekend’s launch of the new Music experience is just the start, and it plans to roll out more music across the platform over time.
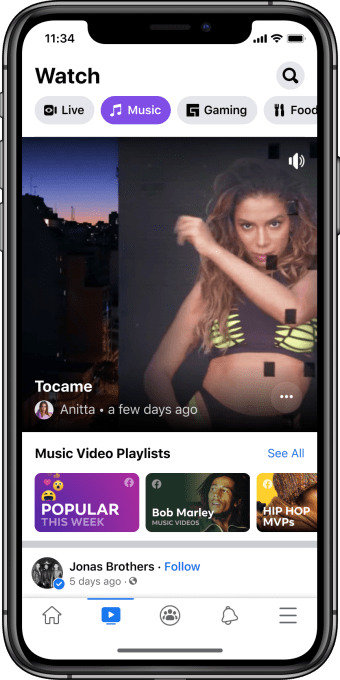
Image Credits: Facebook
Facebook’s launch of music videos is seen as a significant challenge to YouTube, which accounted for 46% of the world’s music streaming outside of China as of 2017, according to a report from IFPI. YouTube, around that time, also claimed more than 1 billion music fans came to its site to connect with music from over 2 billion artists.
More recently, YouTube reported it had paid out more than $3 billion to the music industry in 2019. The music labels, however, have shown interest in an alternative to YouTube, which they feel doesn’t pay enough. The financial terms of Facebook’s deal with the labels were not disclosed.
Though Facebook had deals with music labels before now, those were more limited. Artists from major labels, for example, weren’t able to share full music videos due to licensing rights — they could only post a short preview. The change to include full videos could significantly impact how much time users spend on Facebook in the months ahead.
The launch follows a month-long Facebook advertiser boycott over issues around hate speech on the platform, which some brands have chosen to continue with, reports say. But the music video launch was not timed to encourage an advertiser return. According to documents previously reviewed by TechCrunch, the date of August 1, 2020 had been the planned launch date for some time.
The videos are now one of several ways artists can connect with fans on Facebook, as the company had already rolled out tools that allowed artists to promote new releases with custom AR effects and Music Stickers, host live-streamed Q&As on Facebook Live and raise money for important causes through the donate button in Live and Stories.
“Artist/Fan connection on Facebook is deeper and more authentic because of tools like Stories, Live and custom AR effects. Official music videos are re-born in that setting — they become part of the way people express identity and mood and bring a new dimension to the artist storytelling that happens on our apps every day,” said Tamara Hrivnak, VP of Music Business Development and Partnerships at Facebook.
Behold, the Opple Watch. Many have borrowed heavily from Apple’s wearable, but few, if any, have done so as brazenly as Oppo. Sure Fitbit received some guff for the squircle hardware design of its Versa line, but it’s not useful to get too hung up on those vague similarities — there are, notably, relatively few geometrical options for hardware makers looking to move outside the traditional circle watch face.
But based on the press material, the Oppo Watch is — to put it gently — a dead ringer for the best-selling smartwatch. There are some key differences, of course. The first and biggest is the fact that the device runs Wear OS, Google’s oft-neglected wearable operating system. Also of note is the “dual curved screen,” which allows the watch face to monopolize more space on the device, with a 73% screen-to-body ratio on the 45mm version and 65% on the 41mm. Those displays are 1.91 and 1.6 inches, respectively.
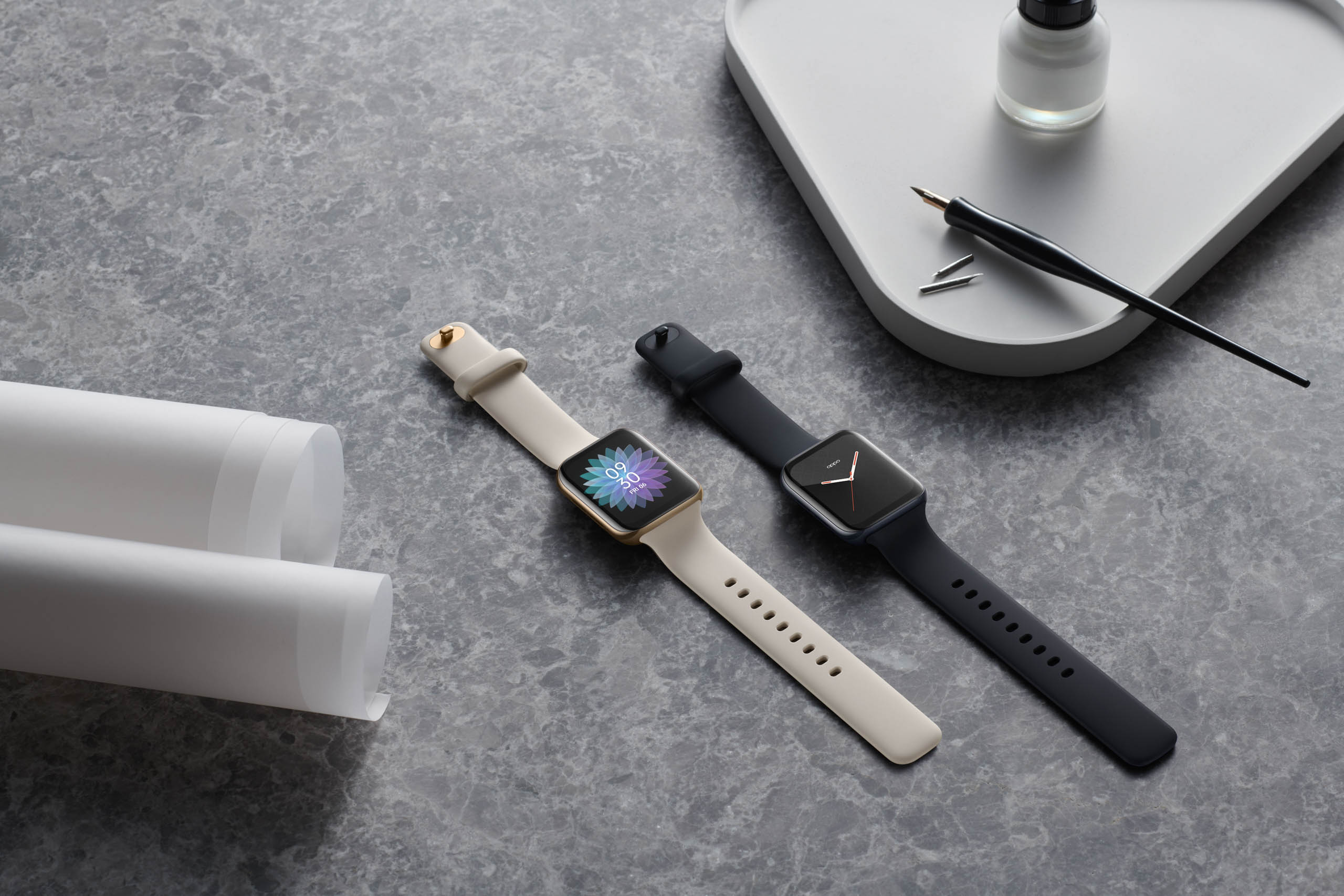

There’s a Wi-Fi and LTE version of the larger model, and both feature GPS+GLONASS tracking, along with heart-rate monitoring and sleep tracking. The battery is 430mAh on the big one and 300mAh on the smaller. The former should get around 36 hours of life on a charge, according to the company, charging back up to full capacity in about 75 minutes. There’s also a battery-saver mode that should keep it alive for a few weeks.
The watches are available starting today in select markets. If you’re in the market for a Wear OS watch, you have a lot of choices, all of which are significantly less likely to be mistaken for an Apple Watch.
CRISPR tech startup Mammoth Biosciences is among the companies that revealed backing from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Rapid Accleration of Diagnostics (RADx) program on Friday. Mammoth received a contract to scale up its CRISPR-based SARS-CoV-3 diagnostic test in order to help address the testing shortages across the U.S.
Mammoth’s CRISPR-based approach could potentially offer a significant solution to current testing bottlenecks, because it’s a very different kind of test when compared to existing methods based on PCR technology. The startup has also enlisted the help of pharma giant GSK to develop and produce a new COVID-19 testing solution, which will be a handheld, disposable test that can offer results in as little as 20 minutes, on site.
While that test is still ind development, the RADx funding received through this funding will be used to scale manufacturing of the company’s DETECTR platform for distribution and use in commercial laboratory settings. This will still offer a “multi-fold increase in testing capacity,” the company says, even though it’s a lab-based solution instead of a point-of-care test like the one it’s seeking to create with GSK.
Already, UCSF has received an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) from the FDA to use the DETECTR reagent set to test for the presence of SARS-CoV-2, and the startup hopes to be able to extend similar testing capacity to other labs across the U.S.
The U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) is revealing the first beneficiaries of its Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) program, and San Mateo-based Helix is on the receiving end of $33 million in federal funding as a result. Helix is a health tech startup founded in 2015 that focuses on insights derived from personal genomics, but the company has also developed a COVID-19 test that detects the presence of SARS-CoV-2 using RT-PCR methods.
The funding will be used to support Helix’s efforts to scale its COVID-19 testing efforts, with the aim of achieving a rate of 100,000 tests per day by this fall, and then extending the throughput capacity even further after that. Helix’s test got FDA Emergency Use Approval (EUA) earlier this month, and has since been available nationally across the U.S., promising “next day” results.
Helix was also filed for an EUA for a second type of test, an NGS test that offers higher throughput for more testing volume, as well as increased sensitivity towards actually detecting the presence of the virus to avoid false negatives. This test, if approved, will be key to helping Helix achieve that much greater scale of testing capability that is the ultimate aim of the RADx program.
That second test system currently seeking approval would be able to process as many as 25,000 tests per day, and it uses a different method that would also help reduce the strain on the supply chain.
News broke last night that Affirm, a well-known fintech unicorn, could approach the public markets at a valuation of $5 to $10 billion. The Wall Street Journal, which broke the news, said that Affirm could begin trading this year and that its IPO options include debuting via a special purpose acquisition company, also known as a SPAC.
That Affirm is considering listing is not a surprise. The company is around eight years old and has raised north of $1 billion, meaning it has locked up investor cash during its life as a private company. And liquidity has become an increasingly attractive possibility in 2020, when new offerings of all quality levels are enjoying strong reception from investors and traders who are hungry for equity in growing companies.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. You can read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
But $10 billion? That price tag is a multiple of what Affirm was worth last year when it added $300 million to its coffer at a post-money price of $2.9 billion. There were rumors that the firm was hunting a far larger round later in 2019, though it doesn’t appear — per PitchBook records — that Affirm raised more capital since its Series F.
 This morning let’s chat about the company’s possible IPO valuation. The Journal noted the strong public performance of Afterpay as a possible cognate for Affirm — the Australian buy-now, pay-later firm saw its value dip to $8.01 per share inside the last year before soaring to around $68 today. But given the firm’s reporting cycle, it’s a hard company to use as a comp.
This morning let’s chat about the company’s possible IPO valuation. The Journal noted the strong public performance of Afterpay as a possible cognate for Affirm — the Australian buy-now, pay-later firm saw its value dip to $8.01 per share inside the last year before soaring to around $68 today. But given the firm’s reporting cycle, it’s a hard company to use as a comp.
Happily, we have another option to lean on that is domestically listed, meaning it has more regular and recent financial disclosures. So let’s how learn much revenue it takes to earn an eleven-figure valuation on the public markets by offering consumers credit.
Affirm loans consumers funds at the point of sale that are repaid on a schedule at a certain cost of capital. Affirm customers can select different repayment periods, raising or lowering their regular payments, and total interest cost.
Synchrony offers similar installment loans to consumers, along with other forms of capital access, including privately-branded credit cards. (Verizon, TechCrunch’s parent company, recent offered a card with the company, I should note.) Synchrony is worth $13.5 billion as of this morning, making it a company of similar-ish value compared to the top end of the possible Affirm valuation range.
Like many industries with a high concentration of wealth — and the careers that help professionals accumulate it — investment firms have a severe dearth of diversity in their ranks.
Regardless of whether the focus is venture capital, private equity or any other investment asset class, the firms are replete with white men. Though there have been some modest efforts of late to push for diversity, particularly in VC, these have yielded single digit percentage changes at best — and nothing at worst. Only 9% of investment decision makers in VC today are women; just 2% are Black.
Some firms have made reasonable inroads on this problem with good intentions. Based on my search experience recruiting investment professionals, I would guess that at least half of those searches were for clients with a strong preference to hire a “diverse” candidate. The Black Lives Matter movement has recently advanced the dialogue even further and has shined a light on underrepresentation in VC more than ever. “How do we increase our pipeline of diverse candidates?” is a question I heard frequently before 2020, but in past weeks this has become a chorus. Unfortunately, if solving this problem were as easy as telling a recruiter you want more diversity, it might have been solved long ago.
Below are a few common pitfalls we see in our searches with VC firms in particular, as well as some thoughts on how firms can improve their hiring processes, in order to work toward having more diverse representation within their investing teams.
The most common reason I see for hiring processes leading to a slate with primarily white male candidates is because the criteria my client views as required almost completely precludes the possibility that the candidate slate will be diverse.
Taken as a given that women and minority men are not well-represented at senior levels in VC, any job spec that asks for a candidate to have seven to 10 years of experience in the industry, or a large number of board seats or investments led, will mean that the pool of “qualified” candidates will consist of mostly white men. This has historically been referred to as the “pipeline problem” and it’s an increasingly well-studied concept that academic literature is beginning to point to as a bias that pushes the onus of hiring minorities away from the hiring manager and on to the candidate pool. Even for firms that remain committed to hiring underrepresented groups without making adjustments to their criteria, the result is a zero-sum game where proven minority investors rotate from firm to firm, and an outcome that does not increase diversity in the industry as a whole.
VC firms seeking to improve their diversity have to recognize that great comes in many forms. By crafting broader specs and really thinking about the qualifications for their investing roles, a whole new talent pool opens up. To see that new pool of talent though, firms must first determine what characteristics are relevant to the role, and avoid tenure (or other tenure stand-ins) as the main criteria. VC investing is as much an art as a science; firms should decide what personal traits make somebody strong in their organization and why. How would a different viewpoint be additive to sourcing or diligence discussions?
Firms then need to commit to interviewing for those traits and perspectives, and assessing candidates along those same lines. One VC firm I worked with interviewed dozens of candidates before they realized that their process focused too much on financial acumen and not enough on the other factors they felt would make somebody a strong venture capitalist, resulting in a final slate of safe, “qualified,” and mostly nonminority candidates.
We reworked our process, and theirs, to interview for different criteria moving forward. We asked about overcoming hardships and about risks taken, and we got a sense for what type of impact that person made in whatever organization they came from rather than just asking about deals and transactions. It should be no surprise that the candidates with noninvesting backgrounds are performing much better in the process now, and the value they’d add to the organization more clear, even though the interviewers and the roles are the same.
A broad spec and a team committed to hiring diverse talent, and interviewing appropriately, are great starting points. But then there is much more to do. Affinity bias is a well-known phenomenon that many investors are likely aware of, but it is pernicious in hiring settings and can be a serious challenge to overcome. Affinity bias in hiring is when a person or group of people prefer a candidate who looks, talks, acts or has a similar background to them.
In the case of hiring candidates with diverse backgrounds, affinity bias may be the tallest hurdle. In VC, the job is in many ways to seek common ground with the people you talk to. Good VCs are relationship builders — with entrepreneurs, other VCs and strong executives they want to recruit into their portfolio companies. But most investors are white people from affluent communities who attended elite universities and have worked at top-tier banks or consulting firms. In some cases there may have been a stint at another top-tier institution, be it a technology company or another investment firm.
White men are more likely to have these backgrounds. In a hiring process, white male VCs will naturally find ways to connect with candidates with similar backgrounds (i.e., other white men), in contrast to candidates with none of those same experiences, even when the candidates with other backgrounds are equally qualified for the role.
Affinity bias can be very subtle. It is human nature to feel the conversation was easier with somebody who in many ways has led the same life you did. It can feel somewhat logical even: The critique of the nonwhite or nonmale candidate is never as obvious as “They didn’t go to Stanford” or “They don’t belong to my country club.” Rather, it is often expressed as something softer and subjective — a seldom-articulated criteria of cultural fit. “Our culture is different from the place they work” is the most common. “I’m not sure they have the drive” is another, or “They don’t have an X-factor.” Now, these critiques can be completely legitimate.
A candidate may indeed be a bad fit for the culture of the firm because, for example, their prior employer was a gigantic corporate machine reliant on extraneous processes and they are interviewing for a role at a small entrepreneurial organization. But sometimes, particularly when interviewing candidates from different backgrounds, culture fit is a mask for affinity bias, and VCs (like all interviewers) need to be conscious of this tendency.
Investment firms almost always try to make a hire through their own network before leading a full search, and even before posting a job as being open anywhere online. This has become such an ingrained behavior that it is often discussed as a best practice. Unfortunately, “hiring through our network” almost certainly means the slate of candidates that a firm considers at the outset is going to be heavily nondiverse. Unless a firm (or to broaden this guidance, an organization) is already diverse across multiple vectors, then beginning a search by canvasing the firm’s own network is highly unlikely to yield a “diverse” candidate. This seems innocuous but it can actually be harmful to the odds that the firm ever hires a candidate from an underrepresented group. Why? There is another bias at work, the status quo bias.
Studies have shown that people tend to make choices that favor the status quo. Creating a balanced slate of choices is critical to avoid disfavoring minority candidates inadvertently. One study showed that having multiple women or Black candidates on a finalist slate increased the odds that the selected would be a minority by 70x-100x. But if a group of interviewers meets five white men through their networks before they meet anybody else, it is going to take an disproportionate number of underrepresented minority candidates to overcome the group’s bias toward hiring the “status quo” of the white men they met at the outset of the search.
At True Search, we recently audited one of our own searches to look for candidate-selected markers of their identity. We compared our pool of candidates to the NVCA diversity data from 2018. Compared to the industry averages, our pool of candidates was half as white and twice as female as the industry at large. I am not sharing that data as an advertisement for True Search, and in fact we strive to do more and are working on multiple programs to increase our networks with diverse candidate pools. The point is, when a VC firm uses a search firm or any outside consultant for a search, the pool of candidates is going to be much more diverse than if that VC firm simply calls up the people in their network, who probably are not all that diverse.
A commitment to hiring more talent with underrepresented backgrounds is great; actually doing it is even better. Many studies have shown that diversity improves the performance of a team, but the onus is on the organization to foster an environment where those viewpoints are appreciated. In my discussions with VCs who are minorities, they point out that once they are in the door of the firm they still face challenges that white male colleagues don’t.
They are less likely to have mentors who share their backgrounds, and investing is largely an apprenticeship business. If they did not come from Stanford or Harvard, they are less likely to see deals that come through the sorts of personal networks that the firm is likely accustomed to seeing. If they came from a noninvesting background, they may be taken less seriously when presenting investment ideas to the team of career investors. A firm has to support diversity of thought once it is in the door, or the contributions of those team members may be unappreciated.
Firms can do many things to foster strong talent from diverse backgrounds once they are in the organization. Minority investors have shared some great ideas with me as I was thinking through this article, so these suggestions aren’t just my own. Underrepresented groups have historically (in the short history of such groups having any significant representation in the investing world) formed mentorship networks that transcend the walls of a given firm, such as Latinx VC, BLCK VC and All Raise.
VC firms should build as much connectivity with those sort of networks as possible. This will not only increase the odds that a firm will see more candidates from underrepresented groups, but it will also mean that the firm can play a role in finding strong mentors for their diverse talent throughout their career. Those networks can be built through small individual actions like attending and sponsoring events, or sharing job postings in the firm and portfolio with those networks.
VC firms can also help to jump-start a hire’s network in venture. Imagine a scenario where a firm hires a noninvestor with a unique yet amazing background into an investing role. Their peers all went to Stanford or worked at Facebook and are sourcing their deals through those personal networks. VC firms can use their resources to help close that network gap, such as by setting aside small pools of capital for a seed fund to be deployed by new investors with diverse backgrounds, thereby giving them a boost in early network building. I’ve seen firms deploy this strategy as a way to keep tabs on high potential operators, or on partner-level candidates they want to get to know more before they commit to hiring full-time.
Firms can help train junior talent and better prepare them for future full-time roles in venture by running intern or analyst programs and emphasizing the hiring of underrepresented groups into those roles. Even a part-time gig in VC will give a candidate a leg up in future interview processes, and even if that person goes off to another firm for a full-time role, the network back to that person will remain and could be helpful as a source of (or mentor to) the diverse talent the firm hires in the future.
Americans are rapidly becoming less religious. Weekly church attendance is falling, congregations are getting smaller or even closing and the percentage of Americans identifying as “religiously unaffiliated” has spiked.
Despite all this, now might be the perfect time for church tech companies to thrive.
A combination of COVID-19-induced adoption, underrated demographic trends and pressure to innovate is setting the stage for new successes in the previously sleepy church tech space. Venture dollars are flowing in, and Silicon Valley is slowly showing serious interest in the sector. Hot new startups are finding creative growth hacks to penetrate a difficult market. Major challenges remain for companies in this space, but their odds seem better than ever.
Yes, Americans are going to church less often, but that doesn’t mean they’re not staying spiritual. In fact, the percentage of Americans identifying as “spiritual but not religious” has grown faster than any other group in this Pew survey on religiosity. This fact is reflected in other data. For example, the percentage of Americans that pray daily or weekly has stayed fairly flat even as overall religiosity declined. This opens up two distinct opportunities, as well as two challenges.
Opportunities:
Challenges:
Rapidly growing startups in the space are deftly navigating this landscape and taking advantage of these trends.
BERLANGGANAN VIA EMAIL