No one wants to be the maintenance worker who has to hike through half a mile of damp hallways just to check the pressure gauge on a valve somewhere. LiLz makes it possible to keep an eye on such inconvenient physical interfaces remotely with a clever and practical application of machine learning.
The Japanese (specifically Okinawan) startup has been around for a little while — in fact our colleagues at TC JP have written them up. But despite the seemingly obvious value of its service, it hasn’t quite hit the big time yet. LiLz participated in CES as part of the country’s trade group, along with a bunch more companies listed here.
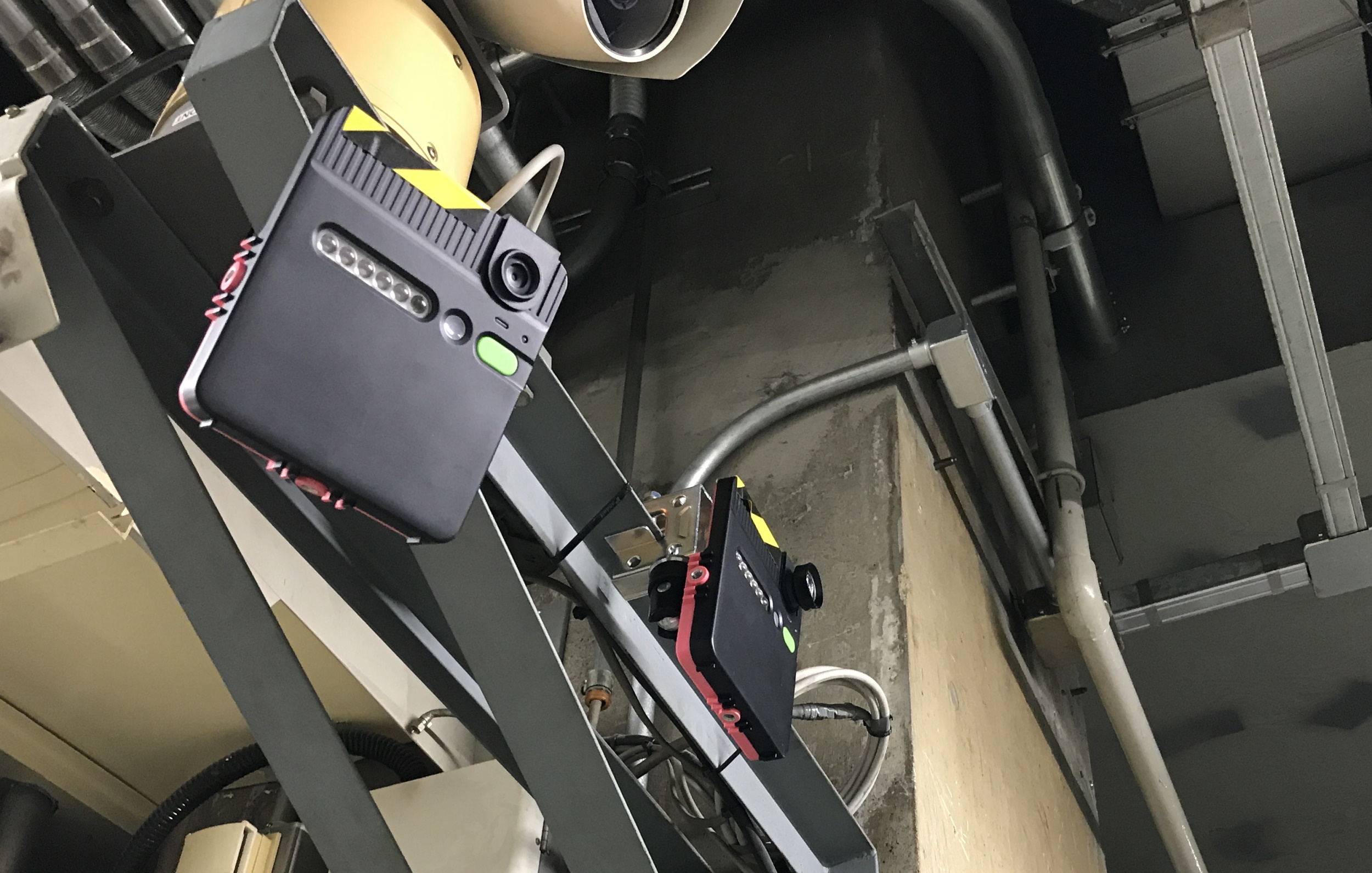
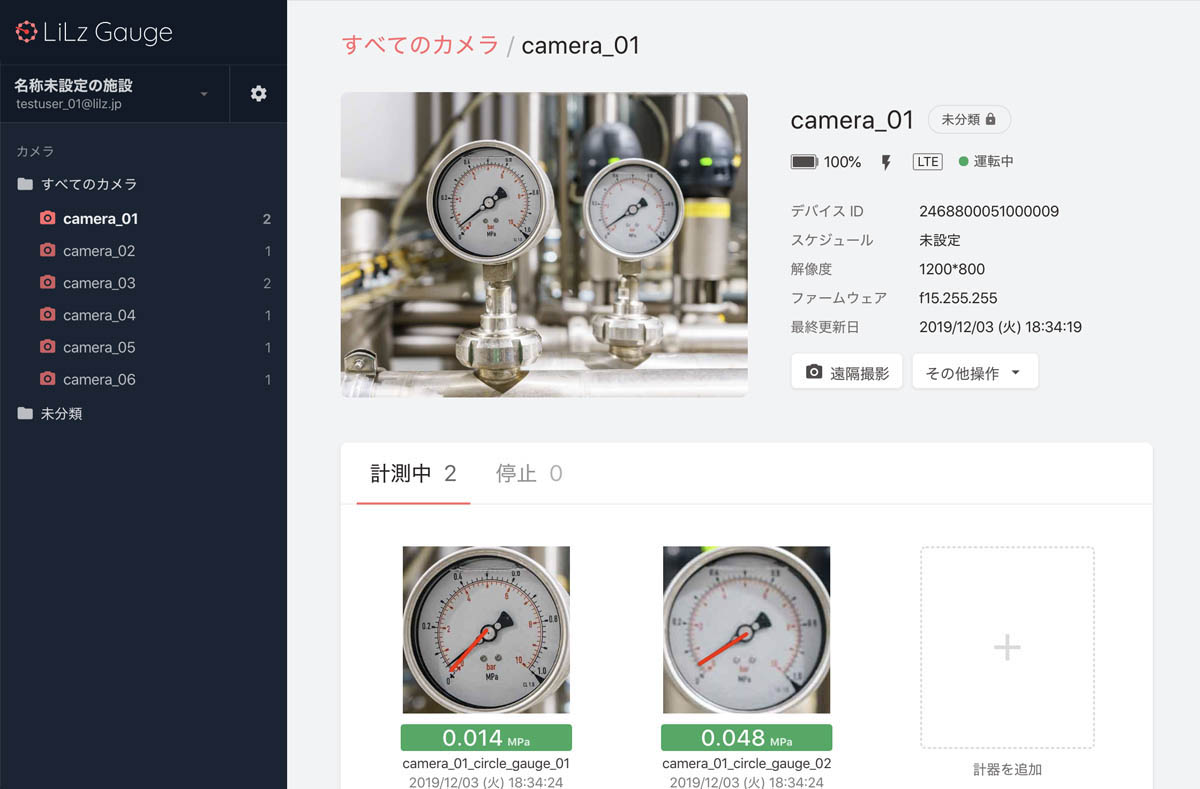
LiLz’s device looks a bit like a chubby tablet without a screen. It’s essentially a camera, light and processing and communications chips packed in with a big battery — enough power to last up to three years.
You mount the device so it can see the gauge or dial in question. After confirming picture and signal, you configure it in the app to interpret what it’s pointed at; it can read circular, semicircular and linear gauges, digital and rolling or analog digit displays, or things like colored warning lights. (The ML involved here is not trivial — I ran across this interesting article while looking into it.)
Once it’s set up, it’ll send readings live or at intervals to a central dashboard, or make them available via API so they can be queried or recorded elsewhere. The data goes out via LTE or Bluetooth.
It’s a solution aimed directly at infrastructure and heavy industry, which often involve lots of legacy equipment located in hard-to-reach places: roofs, underground (but not too deep or the signal can’t penetrate), in labyrinthine factories and warehouses, etc.
Doing daily rounds of these dials is not just dull work for humans, but can be dangerous as well. Using a robot is another way to automate it, but doesn’t a network of IoT devices seem more practical than a quadrupedal bot trucking around constantly?
LiLz CTO Kuba Kolodziejczyk said that the company has been expanding quickly following its debut in 2020 and a $2.2 million Series A round in early 2021.
“We grew from 240 cameras deployed at 34 locations by a few early users before June 2020, to 2000 cameras deployed at 320 locations for over 100 clients now, and expect to grow to 5000 cameras by end this year,” he wrote in an email to TechCrunch. “We now have a few clients using more than hundred cameras at single location.”
They started by targeting basic building management, but now have expanded to chemical and industrial plants, construction and manufacturing sites, public infrastructure and more due to customer demand, he added.
And the capabilities of the device are increasing as well. They’ve mainly been iterating on the software, making it able to be updated remotely, improving accuracy and resilience to disturbance, and adding data sharing and other features. There’s a new explosion-proof (!) version of the hardware as well. Maybe they should get into making phone cases as a side gig.
New products are on the way, one for “sound search” and another for counting of objects in the camera’s view, but both are at a very early stage now. And new capabilities like monitoring float and level gauges, among other things.
Meanwhile, they’ve come to CES to make some outreach to potential clients outside Japan. The show is looking like something of a bust, but maybe a few techs and managers will read this and think “wow, that would be handy.” You can find out more at the shiny new English website here.